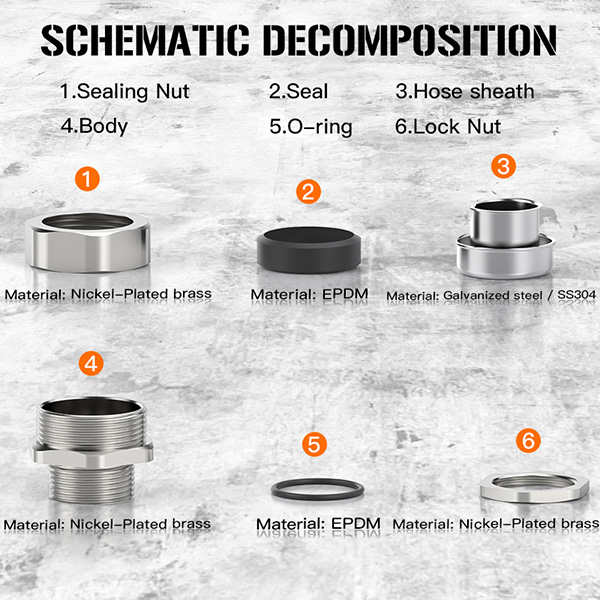
Cable glands are devices used to connect and secure the ends of cables to equipment. They are made of various materials, with steel, brass, or aluminum used for industrial applications.
Connectors designed to withstand dripping water or water pressure utilize synthetic rubber or other types of elastomeric seals. Some types of cable glands also prevent flammable gases from entering equipment enclosures, making them particularly suitable for electrical equipment in hazardous areas.
Currently, there are at least three thread standards:
- Panzergewinde (PG standard)
- Metric thread
- Imperial pipe thread (Imperial system)
This article will focus on the types, materials, functional applications, and selection of appropriate cable glands for PG cables.
What is a Panzergewinde cable gland?
A PG cable connector, also known as a PG cable gland, is a mechanical device used to secure, protect, and seal cables as they enter electrical enclosures or equipment. It is designed to provide strain relief while preventing dust, moisture, and other environmental contaminants from entering the enclosure.
A standard PG cable gland consists of a threaded body, a locking nut, and a sealing insert that grips the cable firmly in place. The term “PG” originates from the German standard Panzergewinde, which refers to an armored thread type commonly used in electrical and industrial installations. Although newer metric thread standards are now widely adopted, PG cable glands remain in use across many applications due to their reliability and compatibility with existing systems.