Key differences between cable glands and cable terminals
When comparing cable glands vs cable terminals, both components play essential roles in electrical and wiring systems — but their functions, materials, and applications are distinctly different. Understanding these differences is critical to ensuring a safe, reliable, and efficient electrical installation.
1. Function and Purpose
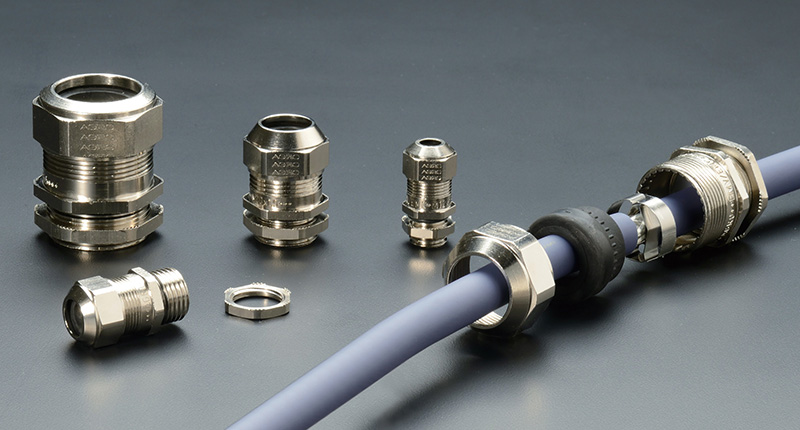
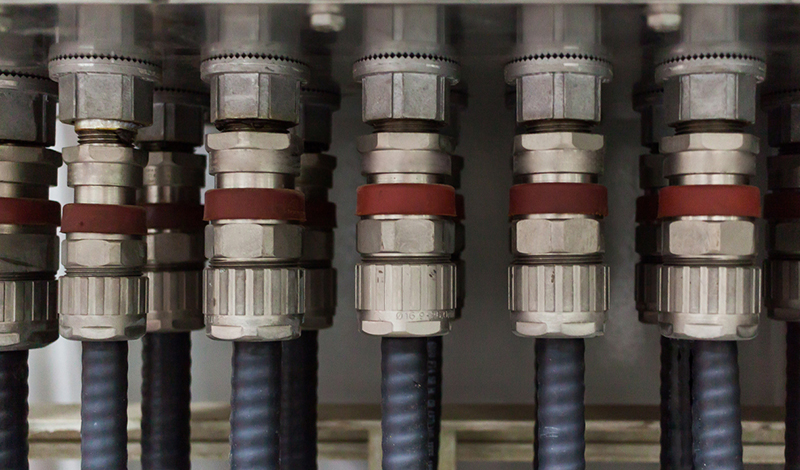
A cable gland is primarily used to secure, seal, and protect cables where they enter equipment or enclosures. It provides strain relief and environmental protection against dust, moisture, vibration, and mechanical stress.
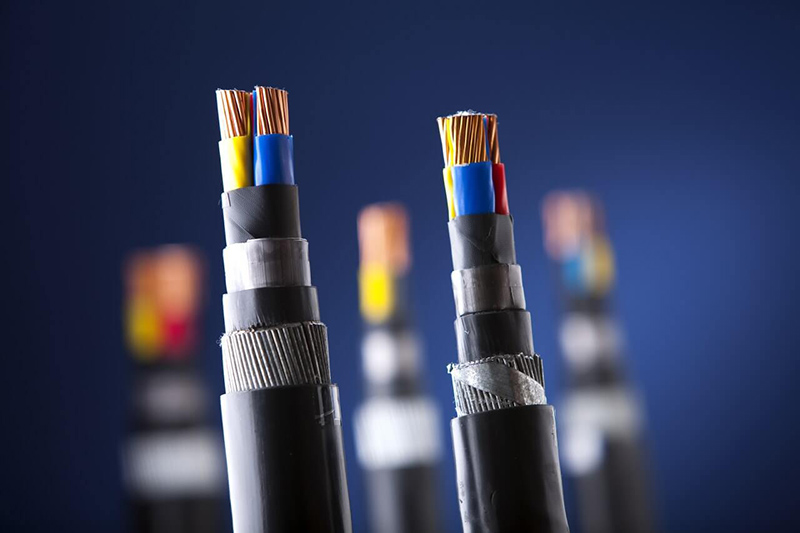
A cable terminal, by contrast, is designed to connect the end of a cable to another electrical component — such as a switch, socket, circuit breaker, or another cable — to ensure proper electrical conductivity and signal transmission.
2. Design and Structure
Cable glands typically feature a threaded body that allows them to be fastened securely to junction boxes, control panels, or enclosures. Many also include integrated sealing elements made of rubber or plastic to ensure a watertight connection.
Cable terminals, on the other hand, are available in multiple configurations such as ring terminals, spade terminals, pin terminals, and butt connectors, each designed to create a stable and conductive electrical connection.
3. Material Composition
Cable glands are commonly made from brass, stainless steel, aluminum, or durable plastic, depending on the application environment. Brass cable glands, in particular, offer superior corrosion resistance and strength, making them ideal for industrial or outdoor use.
Cable terminals are usually produced from copper, aluminum, or stainless steel, materials chosen for their high electrical conductivity and mechanical reliability.
4. Application and Environment
Cable glands are typically used in industrial, marine, or outdoor environments, where cables are exposed to harsh weather conditions or hazardous materials. They provide both mechanical stability and environmental sealing.
Cable terminals are generally used inside electrical panels, control systems, and electronic devices, where they ensure safe, low-resistance electrical connections.
Both are indispensable in modern electrical systems, working together to ensure safety, performance, and durability across a wide range of applications.